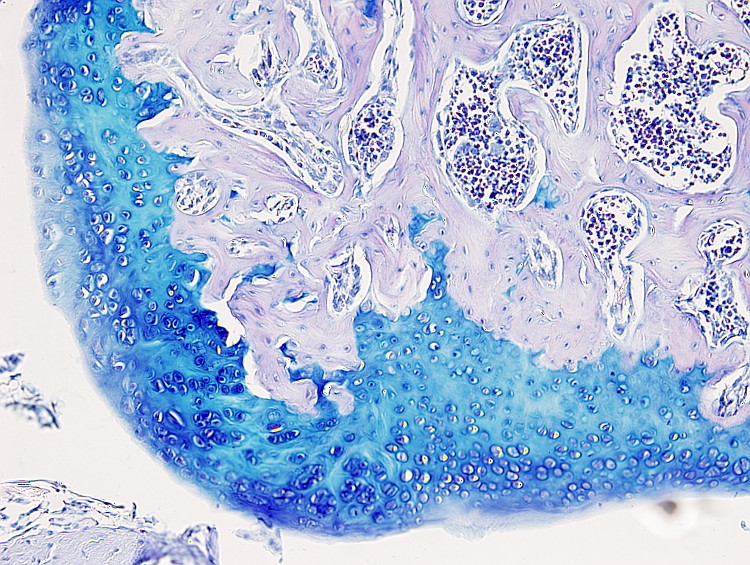
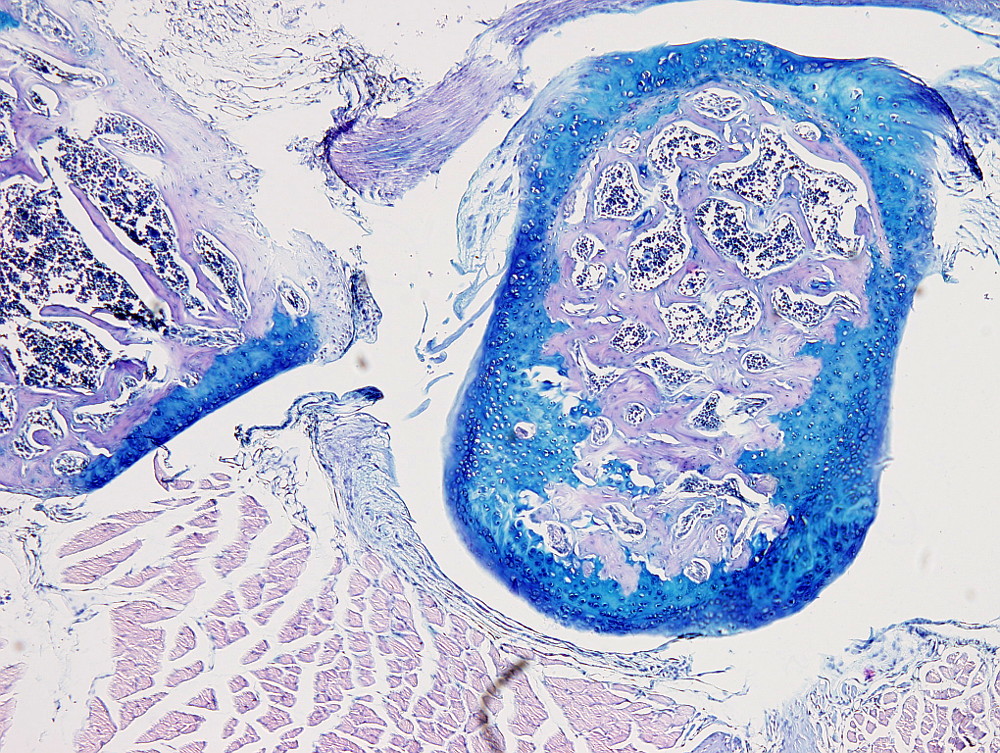
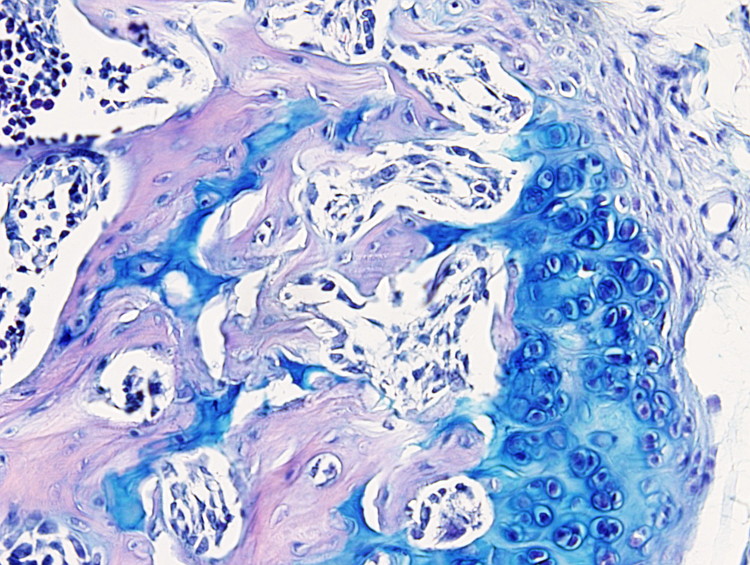
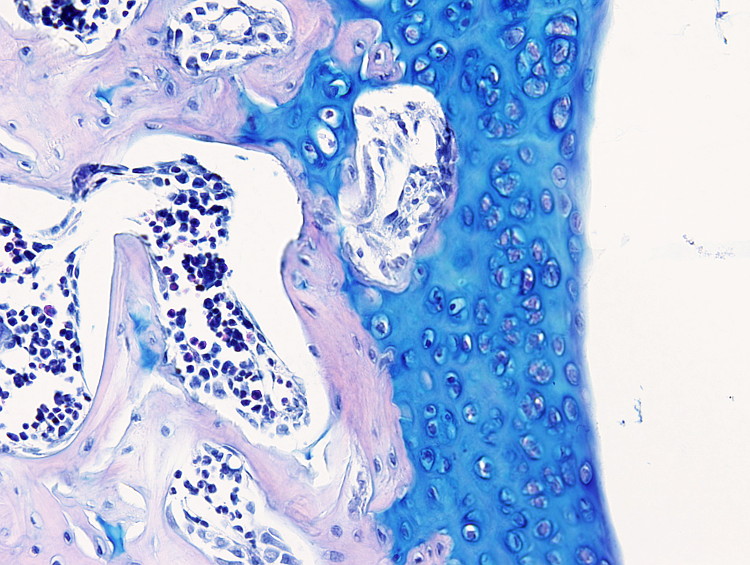
This staining procedure is useful to label cartilage, particularly the articular cartilage, since the cartilage extracellular matrix is stained in blue. It is also performed to label mucous cells, such as goblet cells of the intestine and respiratory epithelium, and mucous cells of the salivary glands.
Procedure
Modified by Elisa Inés Sánchez
8 µm sections from paraffin embedded samples are used. The sections are attached to gelatin coated slides.
1.- 2x10 min in xylene
2.- 2x10 min in 100º ethanol
3.- 10 min in 96º ethanol
4.- 10 min in 80º ethanol
5.- 10 min in 50º ethanol
6.- 5 min in ditilled H2O
7.- 15 min in Alcian blue pH 2.5
1 g Alcian blue (CI 74240) + 3 ml acetic acid + 97 ml distilled H2O.
8.- 15 min in distilled H2O
9.- 5-10 min in Mayer's Hematoxylin
10.- 15 min in tap H2O. Differentiation.
11.- 2x5 min in distilled H2O
12.- 1 to 2 min in 0.2 % yellow eosina (in distilled H2O)
The eosin is an acid dye that binds to the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix elements.
Three types of eosin can be used: yellow eosin (CI 45380), bluish eosin (CI 45400) and alcohol soluble eosin (CI 45386). The yellow eosin is most used.
13.- A few seconds in 70º ethanol. Differentiation.
The intensity of the staining can be modulated in the 70º ethanol differentiation step. A few drops of acetic acid can be added.
14.- 20s in 96º ethanol
15.- 2x3 min in 100º ethanol
16.- 2x10 min in xylene
17.- Mounted and coverslipped
Results
Cytoplasm: pink.
Nuclei: dark purple.
Cartilage: blue.
Mucous cells: blue.
Mastocytes cytoplasm: blue.
Notes
The pH of the Alcian blue staining solution is adjusted to 2.5. Check before the staining step.
Keep in mind that the Alcian blue staining is progressive, that is, the the color intensity increases with the staining time. For example, 10 min of staining time for articular cartilage is enough.
Acid fixatives result in better staining for eosin, whereas fixatives containing picric acid improves the staining overall. The decalcification processes may affect the staining if they use strong acids.
Eosin is highly soluble in water. An over-staining with eosin may be reverted with long washes in water.
If xylen (step 16) turns whitish, it is caused by a poor dehydration. Then, sections need to go back in the procedure until 70º, or even eosin, and dehydrate again.
Although the most used is Mayer's hematoxylin, other types of hematoxylin can be used.
Products
Xylen
50º, 70º, 80º, 90º, 96º y 100º ethanol
Alcian blue (CI 74240)
Mayer's hematoxylin
Yellow eosin (CI 45380)
Acetic acid
Distilled H2O
Tap H2O
Mounting medium
Labware
Staining dishes
Staining racks
Coverslips