Animal tissues. Epithelium.
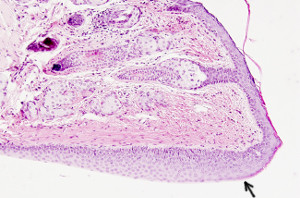
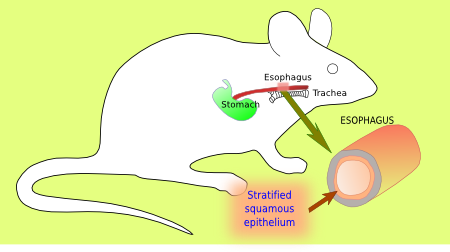
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS

Species: mouse (Mus musculus; mammal)
Technique: haematoxylin-eosin, 8 µm thick section, paraffin embedding.
The stratified squamous epithelium is similar to the keratinized stratified squamous epithelium, but it lacks stratum corneum and stratum granulosum (see also figure 1). Once the contact to the basal lamina is lost, basal stratum cells change from rounded to flattened shapes as they move toward the surface of the epithelium and detach directly from the stratum spinosum. Nearby gland secretions maintain the free surface wet. That is why protection of a corneum stratum against water loss is not necessary. However, the esophagus shows stratum granulosum and stratum corneum in some species that eat hard and abrasive food. Stratified squamous epithelium can be also found in other body surfaces such as the oral cavity, corneal surface, and vagina.

More images