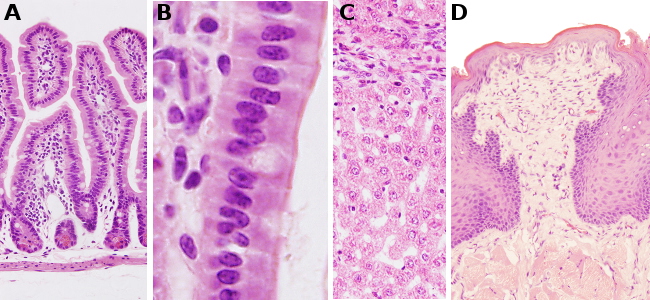
Generally, most cells and extracellular matrix are not colored. Therefore, their microscopic features cannot be easily studied with light microscopes. Dyes are colored molecules used to stain tissues. Depending on the type of dye, specific structures can be stained.
General purpose staining provides an overview of the quality and features of tissues. They may combine two types of dyes. The most widely used general staining combines the basic hematoxylin and the acid eosin.
Procedure
8 µm thick sections from fixed and paraffin embedded samples are processed. Sections are attached to gelatin coated slides.
1.- 2x10 min in xylene
2.- 2x10 min in 100º ethanol
3.- 10 min in 96º ethanol
4.- 10 min in 80º ethanol
5.- 10 min in 50º ethanol
6.- 5 min in distilled H2O
7.- 5-10 min in Mayer hematoxylin
Hematoxylin is not actually a dye. Its oxidized product, the hematein, is the substance that adds the color. Hematein stains the nuclei and large ribosomal aggregates (for example at the rough endoplasmic reticulum)
8.- 15 min in tap water. Differentiation.
9.- 2x1 min in distilled H2O
10.- 0.5 a 2 min in eosin, 0.2 % in distilled H2O
The eosin, an acid dye, stains cytoplasm elements and the extracellular matrix.
Three types of eosin can be used: yellow eosin (CI 45380), bluish eosin (CI 45400) and alcohol soluble eosin (CI 45386). The yellow eosin is most used.
11.- A few seconds in 70º ethanol. Differentiation.
The intensity of the staining can be modulated in the 70º ethanol differentiation step. A few drops of acetic acid can be added.
12.- 20s in 96º ethanol
13.- 2x3 min in 100º ethanol
14.- 2x10 min in xylene
15.- Mounted and coverslipped
Results
Collagen: pale pink.
Muscle: strong pink.
Keratin: intense red.
Cytoplasm: pink.
Nuclei: dark blue to purple (chromatin is the stained element).
Erythrocytes: cherry-like color.
Notes
Acid fixatives result in better staining for eosin, whereas fixatives containing picric acid improves the staining overall. The decalcification processes may affect the staining if they use strong acids.
Eosin is highly soluble in water. An over-staining with eosin may be reverted with long washes in water.
Although the most used is Mayer's hematoxylin, other types of hematoxylin can be used.
Products
Xylene
50º, 70º, 80º, 96º y 100º ethanol
Mayer's hematoxylin
Yellow eosin ((CI 45380)
Distilled water H2O
Tap H2O
Mounting medium
Labware
Staining dishes
Staining racks
Coverslips