Plant tissues. Protection.
EPIDERMIS
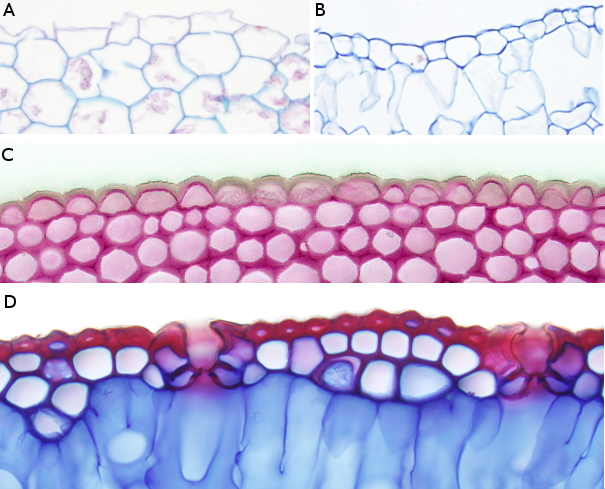
A) Organ: root, epidermis without cuticle.
Species: buttercup (Rannunculus repens).
Technique: paraffin embedding, section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
B) Organ: stem, epidermis with thin cuticle..
Species: potatoe (Solanum nigra).
Technique: paraffin embedding, section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
C) Organ: stem, epidermis with medium size cuticle.
Species: equisetum (Equisetum spp.).
Technique: paraffin embedding, section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
D) Organ: leaf, epidermis with thick cuticle and suberin.
Species: pine (Pinus spp.).
Technique: vibratome section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
Species: buttercup (Rannunculus repens).
Technique: paraffin embedding, section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
B) Organ: stem, epidermis with thin cuticle..
Species: potatoe (Solanum nigra).
Technique: paraffin embedding, section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
C) Organ: stem, epidermis with medium size cuticle.
Species: equisetum (Equisetum spp.).
Technique: paraffin embedding, section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
D) Organ: leaf, epidermis with thick cuticle and suberin.
Species: pine (Pinus spp.).
Technique: vibratome section stained with Alcian blue / safranin.
Ihe epidermis consists of a single layer of densely packed cells that provides the plant with mechanical protection and prevents water lost. The free surface of the epidermal primary cell wall is coated with layer known as cuticle. Cuticle mainly contains cutine and waxes, both are lipidic substances synthesized and released by the epidermal cells. Epidermal cells from the root zone where the water absortion takes place lack cuticle. In other cases, as in potatoe stem, cuticle is very thin. Intermediate thickness of cuticle is found in the mallow stem, and thick and very thick cuticles are present in the epidermis of pine leaves. In this case the epidermal cells also have suberin in their cell wall.
Updated: 2025-02-14. 09:51
